
The use of mobile adblockers has overtaken desktop adblockers globally due to a sharp increase in usage in Asia, according to a study out Wednesday from PageFair. Meanwhile, in the United States, nearly 1 in 5 desktop Internet users is blocking ads, but mobile adblocking remains rare.
Of the 615 million devices globally running adblockers in December 2016, 62 percent — or 380 million devices — were mobile. That’s an increase from 275 million devices using mobile adblockers in December 2015. Overall adblocker usage increased 30 percent worldwide in 2016.
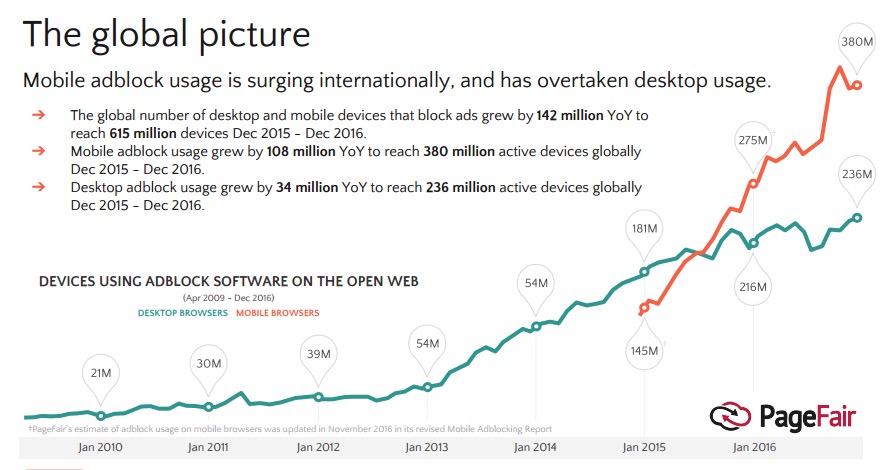
That said, the problem is heavily concentrated geographically: A whopping 94 percent of worldwide mobile adblocking occurs in Asia, and usage grew in the region by 40 percent last year, the study found.
In 2015, Apple released a new version of iOS, its mobile operating system, that would enable iPhone and iPad users to install adblockers. Many publishers and industry observers — including us — thought that the new functionality could have an impact on publishers’ already feeble mobile ad business.While mobile adblocking has clearly caught on in Asia, it has yet to gain a strong foothold in North America and Europe. In the report, however, PageFair cautioned that that could change. (While PageFair’s numbers are generally respected, we should note that the company sells publishers tools to combat adblockers. The company is not a disinterested party; in fact, its business is dependent on people using adblockers.)
“Mobile adblock usage is spreading rapidly due to partnerships between adblocking browsers and device manufacturers & distributors,” the study said. “Mass adoption in North America and Europe will continue organically, but may accelerate unexpectedly if manufacturers or distributors close deals to pre-configure adblock software.”
Even as mobile internet usage surpasses desktop usage, desktop adblockers still reign supreme in North America and Europe — 68 percent of global desktop adblocking occurs on those two continents.

Compare these data points for some countries with large Nieman Lab readerships, first in North America and Europe:
And from Asia and the Middle East:
In an attempt to convince users to turn off their adblockers, some outlets have experimented with preventing users from accessing their coverage unless they turn off their adblockers. The PageFair report suggests that the strategy is largely ineffective, however. The study says that 90 percent of those surveyed who use an adblocker have encountered one of the walls, and 74 percent said they leave websites when they encounter the walls. (Again, PageFair sells a product that promotes a different strategy.)
“Adblock walls are ineffective at motivating most adblock users to disable their adblock software, even temporarily,” the survey said. Unless the website in question has valued content that cannot be obtained elsewhere, an adblock wall is likely to be ineffective at combatting adblock usage at any significant rate.” (Of course, a publisher that doesn’t produce valued and differentiated content has bigger problems than adblockers.)
Despite the emphasis on adblockers, it’s worth nothing that just 11 percent of worldwide Internet users actually use them. And as Internet usage moves away from the open web and toward closed platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat, and other messaging apps, the longterm impact of adblockers may decrease.
The full report is available here.